كتاب Dc Motor M-File
تصميمDc Motor M-File باستخدام الماتلاب مخبر التصميم بإستخدام الحاسب تأليف: أيهم الصالح بناء النموذج الرقمي لمحرك التيار المستمر بإستخدام طريقة أويلر العكسية Key MATLAB commands used in this tutorial are: tf , step , feedback Contents Proportional control PID control Tuning the gains From the main problem, the dynamic equations in the Laplace domain and the open-loop transfer function of the DC Motor are the following. (1)$$ s(Js + b)Theta(s) = KI(s) $$ (2)$$ (Ls + R)I(s) = V(s) - KsTheta(s) $$ (3)$$ P(s) = frac{dot{Theta}(s)}{V(s)} = frac{K}{(Js + b)(Ls + R) + K^2} qquad [frac{rad/sec}{V}] $$ The structure of the control system has the form shown in the figure below. For the original problem setup and the derivation of the above equations, please refer to the DC Motor Speed: System Modeling page. For a 1-rad/sec step reference, the design criteria are the following. Settling time less than 2 seconds Overshoot less than 5% Steady-state error less than 1% Now let's design a controller using the methods introduced in the Introduction: PID Controller Design page. Create a new m-file and type in the following commands. J = 0.01; b = 0.1; K = 0.01; R = 1; L = 0.5; s = tf('s'); P_motor = K/((J*s+b)*(L*s+R)+K^2); Recall that the transfer function for a PID controller is: (4)$$ C(s) = K_{p} + frac {K_{i}} {s} + K_{d}s = frac{K_{d}s^2 + K_{p}s + K_{i}} {s} $$ Proportional control Let's first try employing a proportional controller with a gain of 100, that is, C(s) = 100. To determine the closed-loop transfer function, we use the feedback command. Add the following code to the end of your m-file. Kp = 100; C = pid(Kp); sys_cl = feedback(C*P_motor,1); Now let's examine the closed-loop step response. Add the following commands to the end of your m-file and run it in the command window. You should generate the plot shown below. You can view some of the system's characteristics by right-clicking on the figure and choosing Characteristics from the resulting menu. In the figure below, annotations have specifically been added for Settling Time, Peak Response, and Steady State. t = 0:0.01:5; step(sys_cl,t) grid title('Step Response with Proportional Control') From the plot above we see that both the steady-state error and the overshoot are too large. Recall from the Introduction: PID Controller Design page that increasing the proportional gain Kp will reduce the steady-state error. However, also recall that increasing Kp often results in increased overshoot, therefore, it appears that not all of the design requirements can be met with a simple proportional controller. This fact can be verified by experimenting with different values of Kp. Specifically, you can employ the SISO Design Tool by entering the command sisotool(P_motor) then opening a closed-loop step response plot from the Analysis Plots tab of the Control and Estimation Tools Manager window. With the Real-Time Update box checked, you can then vary the control gain in the Compensator Editor tab and see the resulting effect on the closed-loop step response. A little experimentation verifies what we anticipated, a proportional controller is insufficient for meeting the given design requirements; derivative and/or integral terms must be added to the controller.-
من كتب الإلكترونيات والطاقة - مكتبة كتب تقنية المعلومات.

قراءة كتاب Dc Motor M-File أونلاين
معلومات عن كتاب Dc Motor M-File:
مخبر التصميم بإستخدام الحاسب
تأليف:
أيهم الصالح
بناء النموذج الرقمي لمحرك التيار المستمر بإستخدام طريقة أويلر العكسية
Key MATLAB commands used in this tutorial are: tf , step , feedback
Contents
Proportional control
PID control
Tuning the gains
From the main problem, the dynamic equations in the Laplace domain and the open-loop transfer function of the DC Motor are the following.
(1)$$ s(Js + b)Theta(s) = KI(s) $$
(2)$$ (Ls + R)I(s) = V(s) - KsTheta(s) $$
(3)$$ P(s) = frac{dot{Theta}(s)}{V(s)} = frac{K}{(Js + b)(Ls + R) + K^2} qquad [frac{rad/sec}{V}] $$
The structure of the control system has the form shown in the figure below.
For the original problem setup and the derivation of the above equations, please refer to the DC Motor Speed: System Modeling page.
For a 1-rad/sec step reference, the design criteria are the following.
Settling time less than 2 seconds
Overshoot less than 5%
Steady-state error less than 1%
Now let's design a controller using the methods introduced in the Introduction: PID Controller Design page. Create a new m-file and type in the following commands.
J = 0.01;
b = 0.1;
K = 0.01;
R = 1;
L = 0.5;
s = tf('s');
P_motor = K/((J*s+b)*(L*s+R)+K^2);
Recall that the transfer function for a PID controller is:
(4)$$ C(s) = K_{p} + frac {K_{i}} {s} + K_{d}s = frac{K_{d}s^2 + K_{p}s + K_{i}} {s} $$
Proportional control
Let's first try employing a proportional controller with a gain of 100, that is, C(s) = 100. To determine the closed-loop transfer function, we use the feedback command. Add the following code to the end of your m-file.
Kp = 100;
C = pid(Kp);
sys_cl = feedback(C*P_motor,1);
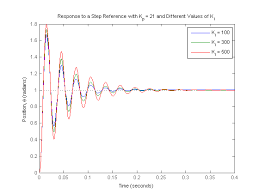
Now let's examine the closed-loop step response. Add the following commands to the end of your m-file and run it in the command window. You should generate the plot shown below. You can view some of the system's characteristics by right-clicking on the figure and choosing Characteristics from the resulting menu. In the figure below, annotations have specifically been added for Settling Time, Peak Response, and Steady State.
t = 0:0.01:5;
step(sys_cl,t)
grid
title('Step Response with Proportional Control')
From the plot above we see that both the steady-state error and the overshoot are too large. Recall from the Introduction: PID Controller Design page that increasing the proportional gain Kp will reduce the steady-state error. However, also recall that increasing Kp often results in increased overshoot, therefore, it appears that not all of the design requirements can be met with a simple proportional controller.
This fact can be verified by experimenting with different values of Kp. Specifically, you can employ the SISO Design Tool by entering the command sisotool(P_motor) then opening a closed-loop step response plot from the Analysis Plots tab of the Control and Estimation Tools Manager window. With the Real-Time Update box checked, you can then vary the control gain in the Compensator Editor tab and see the resulting effect on the closed-loop step response. A little experimentation verifies what we anticipated, a proportional controller is insufficient for meeting the given design requirements; derivative and/or integral terms must be added to the controller.
عدد مرات التحميل : 22447 مرّة / مرات.
تم اضافته في : الثلاثاء , 12 يناير 2016م.
حجم الكتاب عند التحميل : 741.2 كيلوبايت .
تعليقات ومناقشات حول الكتاب:
تصميمDc Motor M-File باستخدام الماتلاب
تصميمDc Motor M-File باستخدام الماتلاب
مخبر التصميم بإستخدام الحاسب
بناء النموذج الرقمي لمحرك التيار المستمر بإستخدام طريقة أويلر العكسية
Key MATLAB commands used in this tutorial are: tf , step , feedback
Contents
Proportional control
PID control
Tuning the gains
From the main problem, the dynamic equations in the Laplace domain and the open-loop transfer function of the DC Motor are the following.
(1)$$ s(Js + b)Theta(s) = KI(s) $$
(2)$$ (Ls + R)I(s) = V(s) - KsTheta(s) $$
(3)$$ P(s) = frac{dot{Theta}(s)}{V(s)} = frac{K}{(Js + b)(Ls + R) + K^2} qquad [frac{rad/sec}{V}] $$
The structure of the control system has the form shown in the figure below.
For the original problem setup and the derivation of the above equations, please refer to the DC Motor Speed: System Modeling page.
For a 1-rad/sec step reference, the design criteria are the following.
Settling time less than 2 seconds
Overshoot less than 5%
Steady-state error less than 1%
Now let's design a controller using the methods introduced in the Introduction: PID Controller Design page. Create a new m-file and type in the following commands.
J = 0.01;
b = 0.1;
K = 0.01;
R = 1;
L = 0.5;
s = tf('s');
P_motor = K/((J*s+b)*(L*s+R)+K^2);
Recall that the transfer function for a PID controller is:
(4)$$ C(s) = K_{p} + frac {K_{i}} {s} + K_{d}s = frac{K_{d}s^2 + K_{p}s + K_{i}} {s} $$
Proportional control
Let's first try employing a proportional controller with a gain of 100, that is, C(s) = 100. To determine the closed-loop transfer function, we use the feedback command. Add the following code to the end of your m-file.
Kp = 100;
C = pid(Kp);
sys_cl = feedback(C*P_motor,1);
Now let's examine the closed-loop step response. Add the following commands to the end of your m-file and run it in the command window. You should generate the plot shown below. You can view some of the system's characteristics by right-clicking on the figure and choosing Characteristics from the resulting menu. In the figure below, annotations have specifically been added for Settling Time, Peak Response, and Steady State.
t = 0:0.01:5;
step(sys_cl,t)
grid
title('Step Response with Proportional Control')
From the plot above we see that both the steady-state error and the overshoot are too large. Recall from the Introduction: PID Controller Design page that increasing the proportional gain Kp will reduce the steady-state error. However, also recall that increasing Kp often results in increased overshoot, therefore, it appears that not all of the design requirements can be met with a simple proportional controller.
This fact can be verified by experimenting with different values of Kp. Specifically, you can employ the SISO Design Tool by entering the command sisotool(P_motor) then opening a closed-loop step response plot from the Analysis Plots tab of the Control and Estimation Tools Manager window. With the Real-Time Update box checked, you can then vary the control gain in the Compensator Editor tab and see the resulting effect on the closed-loop step response. A little experimentation verifies what we anticipated, a proportional controller is insufficient for meeting the given design requirements; derivative and/or integral terms must be added to the controller.
Dc Motor M-File تحميل كتاب
 مهلاً !
مهلاً !قبل تحميل الكتاب .. يجب ان يتوفر لديكم برنامج تشغيل وقراءة ملفات pdf
يمكن تحميلة من هنا 'تحميل البرنامج'

نوع الكتاب : pdf.
اذا اعجبك الكتاب فضلاً اضغط على أعجبني و يمكنك تحميله من هنا:


كتب اخرى في كتب الإلكترونيات والطاقة

ادارة القنوات التلفزيونية والراديو في النت PDF
قراءة و تحميل كتاب ادارة القنوات التلفزيونية والراديو في النت PDF مجانا

شرح short circuit بواسطة برنامج ماثلاب matlab PDF
قراءة و تحميل كتاب شرح short circuit بواسطة برنامج ماثلاب matlab PDF مجانا